
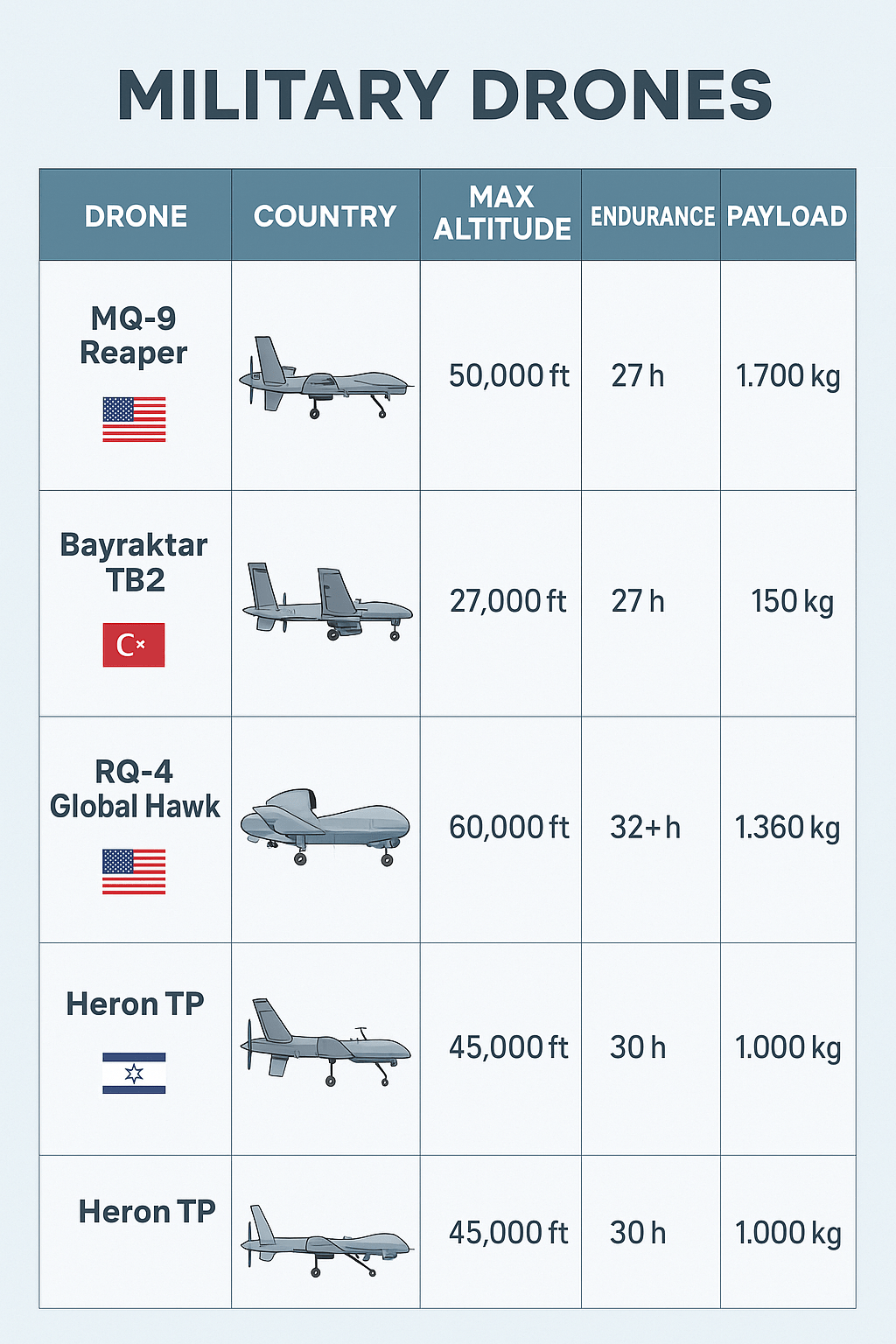
AI Search: Can ChatGPT, Claude, and Friends Displace Google?

In the past 25 years Google has become synonymous with search (handling ~8.5 billion queries per day), powering a $980 billion global ad ecosystem. Now a new wave of AI-powered tools is emerging that deliver conversational answers instead of link lists. ChatGPT (with its new “Search” mode), Perplexity AI, Anthropic’s Claude, You.com, Microsoft’s Bing Chat, and others all tap large language models (LLMs) to synthesize information in real time. These tools often cite sources, support images or voice, and personalize responses, promising faster, more context-aware answers. Early data show explosive growth: Perplexity reported ~15 million monthly users and 159 million visits in March 2025. Even Google sees the threat – a recent survey found 40–43% of users trust AI answers more than traditional search results or ads. Major tech firms (and even Apple’s Safari team) are scrambling to add AI to search to avoid disruption.
Key trends: generative AI tools summarize answers from multiple sources, reducing the need to click through dozens of links. They often provide inline citations or links for fact-checking. Many also integrate images, videos or maps. In one benchmark, privacy-focused Andi Search led in accuracy (87%) over You.com (80%), Google Gemini (71%), ChatGPT (62%) and Perplexity (59%). Voice search and personalized profiles are becoming common, making the experience feel more like a personal assistant than a static search box.
ChatGPT Search (OpenAI)
Launched Oct 31, 2024 after a trial phase, ChatGPT Search embeds web search into the familiar ChatGPT interface. It uses GPT-4o to answer questions with up-to-date info, tapping Bing (and other providers) for live data. Search queries return a concise summary and five top links, plus a “Sources” panel with inline citations. Notably, there are no ads and no paywalls on these links. Since the update, ChatGPT also supports voice input, maps, and shopping queries. (For example, one user finds it useful for local restaurant info on the go.) OpenAI reports ~800 million weekly active users of ChatGPT overall, underscoring its massive reach.
ChatGPT Search has been praised for interpreting natural-language queries (including location or time context) and giving relevant, concise answers with clear links. For instance, a query about 60″ TVs yields a short comparison followed by five relevant retailer reviews. Response quality is generally high, but studies note it tends to produce long answers (≈1,686 characters on average) with many references. A Nielsen Norman Group test found Bing Chat (Microsoft’s version of GPT-4 search) scored lower on user trust/helpfulness than ChatGPT, suggesting strong user confidence in OpenAI’s model. ChatGPT’s fine-tuned models (including “Code Interpreter” etc.) further extend its capabilities. Overall, ChatGPT Search makes search feel like a dialogue – a feature that could unsettle users used to keyword queries and snippet clutter.
Perplexity AI
Perplexity AI (launched 2022) is a web-based AI answer engine that emphasizes speed and accuracy. It combines its own crawler (“PerplexityBot”) with LLMs (such as OpenAI’s GPT or Anthropic’s models) to process queries. Users get a short answer followed by cited sources and a list of relevant links. Perplexity is optimized for complex questions and “LLM-friendly” queries, often giving deeper, more concise explanations than a standard Google result. It routinely provides exactly five citations per answer, a consistent strategy to build trust.
The growth has been staggering. Perplexity handled over 500 million queries in 2024 and more than 100 million weekly by 2025, reaching ~155 million site visits/month (up 205% year-over-year). It claims ~15 million active monthly users, and some reports value it around $18 billion. In practical terms, Perplexity often returns super-quick snippets. A head-to-head SEO study found Perplexity outperformed ChatGPT on certain factual tasks. Its simplicity (just ask and get five sourced points) appeals to researchers and shoppers alike. Unlike Google, Perplexity has no ads or sidebars – the interface is just question and answer. Its open API (free tier) has also enabled integrations (e.g. with Motorola phones) to bring AI answers directly onto devices.
Claude (Anthropic)
Anthropic’s Claude has historically been a safety-focused chatbot, but in 2025 it too gained real-time search. The company announced that Claude can now “search the internet” to access fresh information. In practice, Claude (via its 3.7 Sonnet model on paid plans) will automatically query the web for timely data and weave that into its answers. Crucially, it quotes sources – every time it pulls web info, it adds direct citations. This mirrors ChatGPT’s approach of giving a short summary with links. Early feedback notes that Claude now has up-to-date news and stats, enhancing accuracy for current events and factual tasks.
Like Perplexity, Claude’s web-tool can run multi-step “agentic” searches, refining queries as needed. In tests, Claude tends to give slightly shorter answers than ChatGPT but maintains a safe, factual tone. Its strength is groundedness: by default Claude is trained to avoid hallucinating. With web access, it becomes a more potent research assistant. Anthropic’s launch of a search API signals they believe AI chatbots will be the new interface to information. (In fact, Apple is reportedly eyeing partnerships with OpenAI and Anthropic for exactly this reason.)
You.com (YouChat)
You.com is an AI-powered search engine known for personalization and privacy. It offers several “AI modes” tailored to query types, and a chatbot called YouChat. YouChat can answer recent queries (like ChatGPT) because the underlying search is always live. The engine highlights its customization: users can upvote, downvote, or even block sources, so that over time search results are personalized. You.com also claims an encrypted, ad-customizable platform. Notably, ads are still shown alongside AI summaries – unlike most AI chat results. The AI response panel is text-focused (with optional images for certain modes), and every answer includes small clickable source links.
Behind the scenes, You.com’s models include fragments of GPT and open models; it also integrates image tools (“YouImagine”) and writing assistants. The emphasis is on a human-friendly interface: auto-complete suggestions, AI “agents” for tasks, etc. In one review, You.com was lauded for balancing LLM answers with a traditional search list, all while giving you control over which sources matter. In a recent ranking, You.com scored 80% on factual accuracy (outperforming ChatGPT and Perplexity). Its drawback? The AI answers tend to be very text-heavy and, because of ads, a bit cluttered. Still, its personalization and source controls set it apart as an alternative model for search.
Bing Chat (Microsoft)
Microsoft’s Bing Chat (Powered by GPT-4, also called “Copilot” or “Bing AI”) is essentially ChatGPT integrated into Bing and the Edge browser. It performs real-time web search and returns answers with embedded citations (footnotes) and “Learn more” links. Importantly, Bing Chat’s interface can include images and videos in answers (Google’s Bard does too). For example, a query about cooking might return a step-by-step answer plus an embedded YouTube video snippet. Unlike ChatGPT, Bing Chat does show ads at the bottom of chat threads.
User studies have been mixed. Nielsen Norman’s recent tests found Bing Chat’s answers were rated less helpful and trustworthy than ChatGPT or Google Bard. Some of this is due to occasional inaccuracies or the presence of ads. But Bing has one advantage: it can generate images on demand (DALL·E style) right in the chat, which ChatGPT cannot (yet). Overall, Bing Chat offers a feature-rich AI search (multimedia, follow-up suggestions, chat history) at the cost of occasional flare-ups of “hallucination” and ads. It’s effectively Microsoft’s bid to lure users from Google by embedding AI everywhere in its browser.
Google Bard / Gemini
Not to be outdone, Google has rolled out Bard (now merged into Gemini) and new AI features in Google Search. Google’s approach is to embed AI answers directly in the search results via “AI Overviews” or SGE. These Overviews provide a quick summary at the top of the page (with bullet points) and a few “About this result” links. Unlike ChatGPT, Google does not explicitly cite sources in those bullet summaries; instead it lists product links or related sites in a carousel. (The full search results still appear below, with ads and organic links as usual.) According to Google, these AI answers already handle over 1.5 billion queries a month globally.
For consumers, Google’s AI mode blends old and new: you still get the Google interface and its 90% market reach, but with AI hints and images. Surveys show many users stick with Google for factual queries (57.8% of US searchers prefer Google over ChatGPT for hard facts). But Google acknowledges the shift – its Search experiments are designed to keep users engaged by “doubling time spent” on AI answers. Privacy and ads remain Google’s focus: AI results are seamlessly monetized like normal search ads, at least for now.
Andi Search (Privacy AI)
Andi is a small but intriguing AI search engine. It bills itself as a “privacy-first, ad-free, factually grounded” engine. Andi’s UI is visually rich: answers often include relevant images and quick-links, and at the top you can toggle between web, image, and video results. Benchmarks suggest Andi’s answers are highly accurate (it scored 87% in one test). Internally, Andi uses LLMs to understand the question and then fetches web sources to back its answer – a hybrid approach to avoid the “hallucinations” of pure chatbots. So far, Andi is free to use and still being refined. Its emphasis on privacy (no tracking or cookies) and on image-enhanced answers shows one future direction for search that Google or others might emulate.
Grok (xAI)
A new entrant is Grok, developed by Elon Musk’s xAI and integrated into X.com (formerly Twitter). Grok describes itself as a “truth-seeking AI” that can do real-time web search for “fresh, relevant data”. In early previews, Grok impresses with blunt, quick answers and even its own quirky humor (it prides itself on being “unfiltered”). Like Bing, Grok can generate images on demand. It taps into Musk’s social network for trending info, which could be a game-changer for real-time news or public sentiment queries. Grok is still very new, but it exemplifies how many AI startups are focusing on open, real-time search integration beyond the Big Tech players.
| Tool (Provider) | Real-time Web Search | Citations / Sources | Multimedia | Personalization & Privacy | Notes / Differentiators |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ChatGPT Search(OpenAI) | Yes – uses web (GPT-4o) | Inline citation links in answers | Text & (some) images | Voice mode; conversation history; Plus features | Largest user base (~800M weekly); no ads; chat-like interface |
| Perplexity AI | Yes – proprietary crawl & LLMs | Always shows ~5 source links per answer | Mostly text (can do some images with API) | Fewer personalization; track usage metrics | Fast, concise answers; ~15M monthly users; 700%+ growth; deep answers |
| Claude (Anthropic) | Yes – accesses live web (Sonnet 3.7) | Provides direct citations for web info | Primarily text (images in development) | Built-in safety filters; emphasis on trustworthiness | Focus on accuracy/safety; designed to avoid hallucinations; enterprise-ready |
| You.com (YouChat) | Yes – up-to-date search with AI | Citations via links in chat / list | Text, plus optional images via YouImagine | Highly personalized (block/vote sources); privacy options | Four AI modes; built-in tools (writing, images); still shows ads |
| Bing Chat (Microsoft) | Yes – GPT-4 integrated with Bing search | In-text footnote links, “Learn more” | Rich – images, videos, and DALL·E creation | Limited personalization; follows Bing privacy (Microsoft) | Built into Edge; includes ads; scored lower in trust than ChatGPT |
| Google Bard / Gemini | Yes – Google Search backend | No explicit citations (uses “About this result” cards) | Images in answers, maps, etc. | Uses Google account history; searches are personalized | AI summaries in normal search; still shows ads; 90% search market |
| Andi Search | Yes – AI-driven web fetch | Cites authoritative web sources | Strong image integration | Privacy-first (no tracking); no ads | Designed to be ad-free and factually grounded; ranked top in an AI benchmark |
| Grok (xAI) | Yes – real-time web + X feed | Typically uncited (aims for direct answer) | Generates images; part of X.com platform | Early stage; “unfiltered” answers, less filtered | New AI by Elon Musk; emphasizes truth-seeking; integrated with social data |
The table above highlights key differences. Notice how all these tools can fetch up-to-the-minute information, unlike classic ChatGPT without a browser or last-year-knowledge. Most provide sources (except Bard/Gemini) so you can verify answers. Many also mix in visual content or voice – for example, Bing and Grok can answer with images. Personalization varies: You.com and Andi emphasize user control and privacy, while Google and Bing leverage your profile.
Disruptive Implications
These AI features could seriously shake up traditional search. If users prefer one-stop, ad-free answers, site publishers lose traffic. AI answers cut out the middleman – there are fewer clicks on organic links. VentureBeat warns that “AI assistants provide direct answers, dramatically reducing click-through to content sites,” threatening the ad-based web economy. Google’s own execs are worried: Apple’s Safari saw search volume drop for the first time ever, and Apple is said to be exploring replacing Google with partners like Perplexity or OpenAI. Even on Wall Street, analysts note that companies like OpenAI (ChatGPT) and Grok could be “search competitors” to watch.
From a user perspective, these tools feel simpler and faster. Instead of sifting through 100 search results, you get an answer snippet. Many users (especially younger ones) are beginning to prefer this: one study found nearly 19% of consumers now use AI tools for search, directly challenging Google’s long-held dominance. Moreover, surveys show people tend to trust AI-generated answers more than paid ads, and 60% of AI search users expect to use them even more in coming months. In short, a sizable shift in user behavior is underway.
Looking ahead, Google is adding its own generative features (Gemini AI Mode) to keep up, but the onus is on them to adapt. For now, tech-watchers expect a hybrid era where conversational AI complements traditional search. Content creators must optimize for both: being featured in AI answers (cited by name) may become as important as ranking on Page 1. In any case, the genie is out of the bottle: AI is rewriting the rules of search, and both users and Google will have to adjust to this new information economy.
Sources: Cited above are recent industry reports and analyses of AI search tools, along with usage statistics from OpenAI and surveys. These provide the data and comparisons summarizing how AI chatbots like ChatGPT, Claude, Perplexity, You.com, etc. stack up against traditional search.
Hello, I am Aman (: Full Time Traveler :) At the age of 41, in April 2023, fueled by my love for travel and the determination not to remain fixed like a tree, I embarked on a bold journey. Having dedicated 17 years to a corporate job, I chose to transition from a full-time employee to a full-time traveler, driven by the desire to break free from the routine and constraints of a conventional life. Along the way, I not only explored the wonders of travel but also uncovered the transformative power of financial freedom. I realized how it could liberate me to lead a life teeming with adventure, purpose, and fulfillment. Through my blogs, I am passionately sharing my story, aiming to inspire and provide valuable guidance to those, like me, who aspire to weave travel into a life overflowing with limitless possibilities.




















Post Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.